

نوع المقالة : بحث
المؤلف
قسم الفیزیاء، کلیة التربیة، جامعة بنغازی، بنغازی، لیبیا.
الملخص
الكلمات الرئيسة
الموضوعات
1. Introduction:
The viscosity is the resistance of a liquid to the displacement of one layer in relation to another layer under the influence of externalforces, or in other words, measuring the resistance of a liquid to flow or internal friction [1]. It is used in a wide range of scientific and technical fields and is also one of the important parameters for quality control in many polymeric process products [2]. Viscosity is the resistance of a substance to flow, it is a measure of the resistance of a fluid to deformation under shear stress. There are two main types of viscosity, kinematic viscosity and dynamic viscosity. Dynamic viscosity, sometimes called absolute viscosity, is obtained by dividing the shear stress by the rate of shear strain. Kinematic viscosity is the measure of the rate at which momentum is transferred through a fluid. It can be obtained from the dynamic viscosity by dividing it by the density of the substance [3]. Polymers are versatile materials that play an important role in a wide range of industrial applications. Polymeric solutions or suspensions lubricate the joints of the human body, give foods a rich, creamy appearance, and provide stability to inks and paints. In these and many other applications, the rheological characteristics of the polymer solution have a decisive influence on the performance and functionality of the product [4]. Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) is a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer that is non-toxic in nature. It is an odorless and tasteless ivory powder that can be easily mixed physically or chemically with other polymers. PVA is considered an environmentally friendly food packaging material that exhibits excellent water absorption, is resistant to chemicals and gases, and has film-forming properties [5]. Very large chains (polymers) contain a variety of functional groups, can be mixed with other low or high molecular weight materials, to be adapted to all applications. Polymers are becoming increasingly important in the field of drug delivery, and advances in polymer science have led to the development of several new drug delivery systems, proper consideration of surface and volume properties can help in the design of polymers for various drugs applications [6]. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), a non-ionic, non-toxic, water-soluble amorphous polymer with high solubility in polar solvents, has been widely used in nanopar-ticle synthesis. Due to its amphiphilic nature, PVP can affect the morphology, stabilizing the discriminating surface, controlling crystal growth, acting as a shape control agent, and facilitating growth of specific crystal faces while preventing further [7]. Aqueous solutions of polyvinylpyrrolidone are used in cosmetics, medicine, pharmacy and have been applied in a wide variety of applications such as blood plasma, medicine, biomaterials, coatings, substitutes, macromolecu-lar and cosmetics additives, because it have low toxicity and high solubility in water. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is characterized as a non-toxic, water-soluble polymer that resists recognition by the immune system. The term PEG is often used to designate polymer chains with a molecular weight of less than 20,000. It is rapidly cleared from the body and has been approved for a wide range of biomedical applications. Due to these properties, hydrogels prepared from polyethylene glycol are excellent candidates as biomaterials. Polyethylene glycol can transfer its properties to another molecule when it is covalently attached to that molecule. This could cause toxic molecules to become non-toxic or hydrophobic molecules to become soluble when coupled to polyethylene glycol [8]. Chemical modification of polymers is one of the methods used to produce new polymeric materials to broaden the application of existing polymers that lack the required properties [9]. The aim of this work is to improve the flow properties of polymers, in particular viscosity, by mixing polymers for use in various fields.
2. Experimental:
2.1 Samples:
Polyvinylalcohol (PVA: 99+40 hydrolysed, Mw 85000 g mol-1), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP has Mw 10000 g mol-1) and polyethylene glycol (PEG with Mw 12000 g mol-1) used were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich GMBH. The samples for this research are divided into three portions, the first consists of 0.7 wt % of polyvinyl alcohol, to which a different concentration of polyethylene glycol ( 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7 wt%) is added, while the second sample is added to the same weight of polyvinyl alcohol, and the same concentration of polyethylene glycol in the first sample, but of polyvinylpyrrolidone( 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7 wt%). The third part of the samples is added to the same weight of polyvinyl alcohol, the same concentration of polyethylene glycol (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7 wt%) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7 wt%) together. One of the concentrations of polyethylene glycol or polyvinylpyrrolidone or both was added to the weight of the polyvinyl alcohol It was heated with stirring for half a second, and all the samples were prepared in this way to obtain a solid samples of polymers, then dissolved in 100 milliliters of nitric acid with a concentration of 70 wt% to give solutions at room temperature (30oC).
The average molecular weight of the samples using the molar mass and Avogadro’s number is calculated for all solid samples from the following equation [10] , [11]:
![]()
Where, Ni is a number of molecules in the polymer and Mi is a molecular weight of the polymer. To determine the flow time of the solutions, the methodology provided by ASTM(1989) was used. The exit time of the solvent as well as the exit time of the other three samples were measured with a capillary glass viscometer. The measured values were expressed in terms of relative (ηr), specific (ηsp), reduced (ηred), and inherent (ηinh) viscosities of all samples as follows[12] , [13]:

where tsolution is is the efflux time of pure solvent and tsolution is the efflux time of the samples. The specific viscosity is given by:
![]()
and ηredis,
![]()
Where C i the mass concentration of polyethylene glycol or polyvinylpyrrolidone or both and inh can be expressed as: Intrinsic viscosity [η] is the relationship between the specific viscosity of a solution and the concentration of the solute, extrapolated to zero concentration.
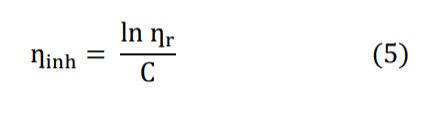
![]()
![]()
[η] can be calculated using equations (6) and (7), but has been calculated in this article using equation (7) [13].
Table 1 includes the molecular weights of the solid samples that were calculated using equation (1), it is clear that the molecular weight of the solid samples containing polyethylene glycol or polyvinylpyrrolidone increases and the molecular weight of the samples containing polyethyleneglycol is higher than that of the samples containing polyvinylpyrrolidone, but the molecular weight of samples containing polyethyleneglycol and polyvinylpyrrolidone together decreases with increasing concentration. The above results indicate the possibility of modifying the molecular weight of the polymers using the mixing method.
After mixing and stirring the polymers by heating for half a second, they were no longer soluble in water, so they dissolved in nitric acid. Figures (1-4) represent the relationships between certain types of viscosity for samples used in research and the concentrations of polymers they contain, where Figure 1 shows is the relative viscosity and concentration, Figure 2 reveals the relationship between specific viscosity and concentration, Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the evolution of intrinsic viscosity and the ratio between reduced viscosity and inherent viscosity by changing the concentration, respectively.
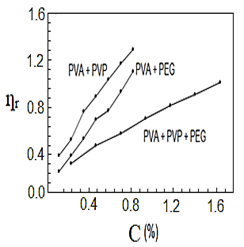
Figure 1. vs. concentration%.
From the figures shown in the results it is clear that the viscosities of the samples of different types increased with increasing concentration [14], exception of intrinsic viscosity which is decreased with increasing concentration [15]. On the other hand the viscosity of the samples containing PVP was higher than that of the samples containing PEG. In all the drawings, the samples made from the three polymers were always lower than the viscosity of the other samples. Figure 1 in [16], Figure ?? in [17] and Figure 3 in [18] indicates an increase in sample viscosity as shown by the results of this study [16] - [18]. It is observed in Figure 4 of [18] that the intrinsic viscosity decreases with increasing concentration, and this is evidenced in Figure in this study [19].
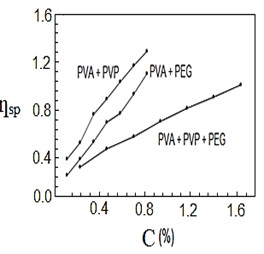
Figure 2. vs. concentration %.
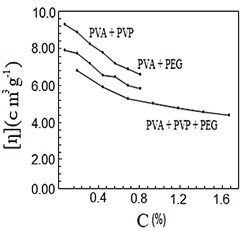
Figure 3. [η] vs. concentration %.
It is clear that the viscosity of polymer solutions can be changed by mixing the polymers in different ways. Note that adding PVP to PVA increases the viscosity of the solution more than its increases by adding PEG to PVA, while adding PVP and PEG together to PVA produces a solution that has a lower viscosity than the previous two solutions, which gives them many uses, there forces according to the results of this research it can be recommended to change the properties of polymers solutions and use them in industrial applications, medical services and scientific studies.
Table 1. The Molecular Weight of Solid Samples.
|
|
PVA (0.7%) |
|
||||
|
|
PVA+PEG |
|
PVA+PVP |
|
PVA+PEG+PVP |
|
|
Concentration |
Mw |
Concentration |
Mw |
Concentration |
Concentration |
Mw |
|
of PEG % |
(g mol−1) |
of PVP% |
(g mol−1) |
of PEG % |
of PVP % |
(g mol−1) |
|
0.1 |
5.73 × 1031 |
0.1 |
4.48 × 1031 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
68600 |
|
0.2 |
9.56 × 1031 |
0.2 |
7.96 × 1031 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
58100 |
|
0.3 |
1.29 × 1032 |
0.3 |
1.07 × 1032 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
58000 |
|
0.4 |
1.56 × 1032 |
0.4 |
1.30 × 1032 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
45500 |
|
0.5 |
1.79 × 1032 |
0.5 |
1.49 × 1032 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
41500 |
|
0.6 |
1.98 × 1032 |
0.6 |
1.65 × 1032 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
38300 |
|
0.7 |
2.15 × 1032 |
0.7 |
1.79 × 1032 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
35700 |
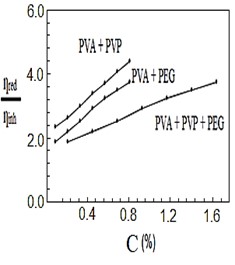
Figure 4. The ratio between ηredand ηinhvs. concentration%.
Funding: None.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data Availability Statement: All of the data supporting the findings of the presented study are available from corresponding author on request.